Hypertension
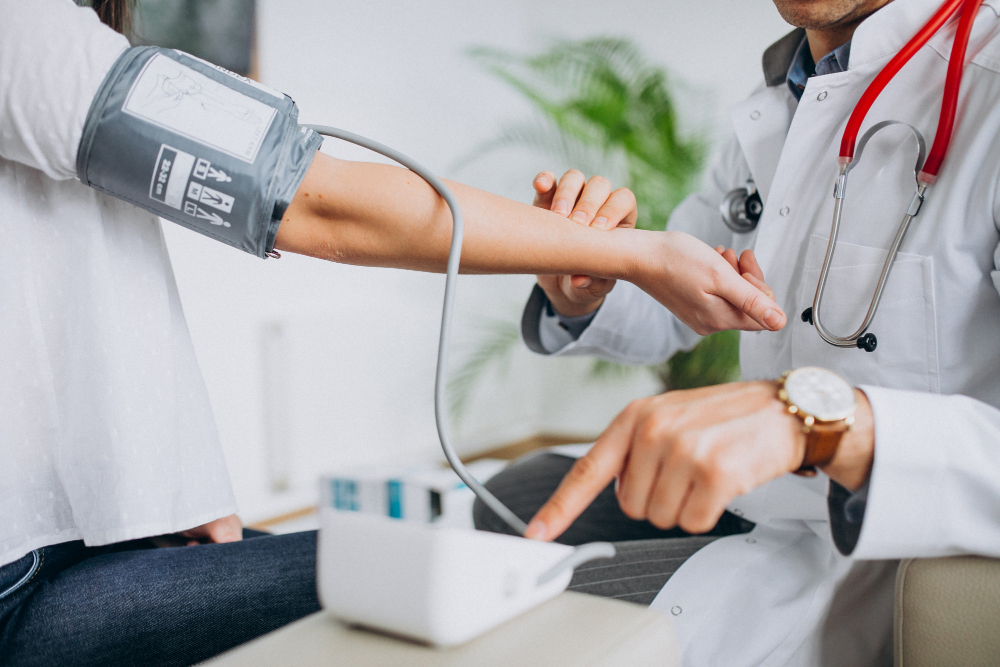

- Hypertension, often referred to as high blood pressure, is a common medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels persistently above the normal range. It is a significant risk factor for various cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.
- Lifestyle factors such as diet high in sodium, lack of physical activity, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can contribute to hypertension. Additionally, genetic predisposition, age, and certain medical conditions such as kidney disease, diabetes, and sleep apnea can also play a role in its development.
- Management of hypertension typically involves lifestyle modifications such as adopting a healthy diet low in sodium, regular physical activity, weight management, smoking cessation, and limiting alcohol intake. In addition, medications such as diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers, and others may be prescribed to help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure are essential to prevent long-term damage to the heart, blood vessels, and other organs.