Diabetes Mellitus
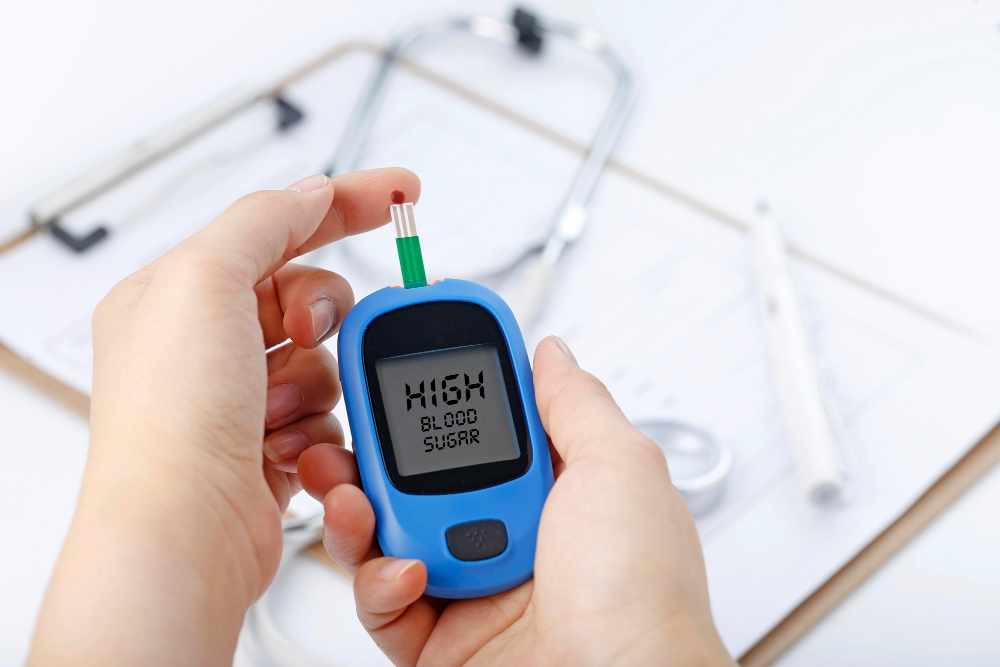
- Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production (Type 1 diabetes) or the body’s ineffective use of insulin (Type 2 diabetes). It can lead to serious complications affecting various organs and systems, including the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
- Risk factors for diabetes mellitus include genetics, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, age, ethnicity, and certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy, while Type 2 diabetes often develops later in life and may be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and insulin therapy.
- Management of diabetes mellitus focuses on controlling blood sugar levels to prevent acute complications such as hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and reduce the risk of long-term complications. This includes regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to a healthy diet, regular physical activity, weight management, medication adherence, and appropriate insulin therapy. Additionally, patients with diabetes benefit from regular medical follow-ups, comprehensive foot care, eye examinations, and screening for complications to maintain overall health and quality of life.