Asthma
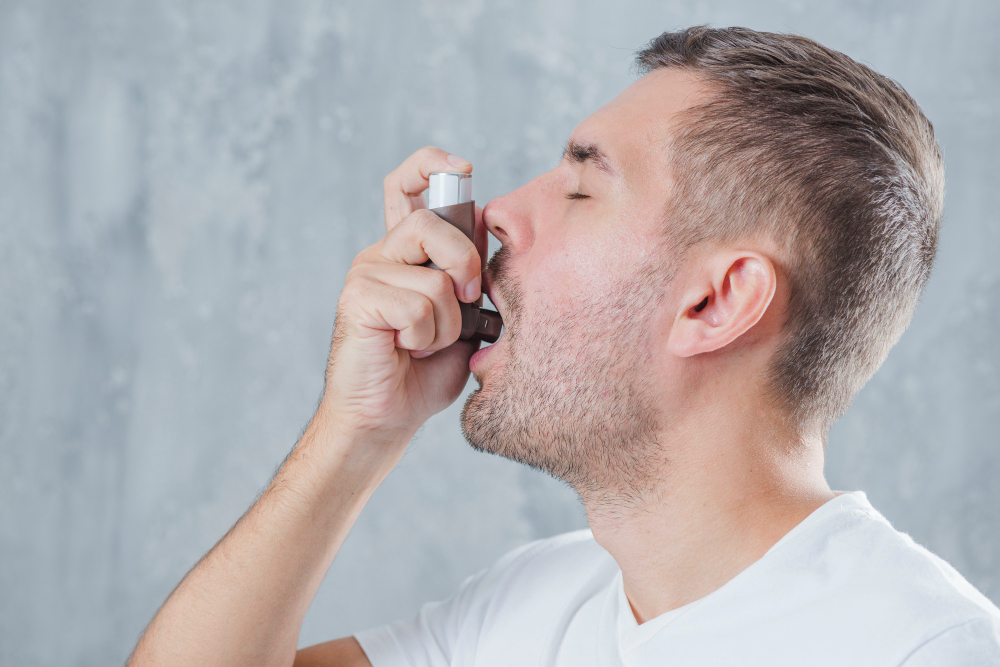

- Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, and chest tightness. These symptoms can vary in severity and frequency, with triggers including allergens, respiratory infections, exercise, and exposure to irritants like smoke or pollution.
- Risk factors for asthma include genetics, allergies, exposure to tobacco smoke during infancy, respiratory infections during childhood, and environmental factors such as air pollution and occupational exposures. While asthma cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed through a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and avoidance of triggers.
- Treatment for asthma typically involves the use of medications such as inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, leukotriene modifiers, and biologics to control inflammation, open up the airways, and prevent asthma symptoms. In addition to medication, individuals with asthma are encouraged to identify and avoid triggers, maintain a healthy lifestyle, use proper inhaler techniques, and develop an asthma action plan with their healthcare provider to effectively manage symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential to ensure optimal asthma control and minimize the risk of exacerbations.