Depression
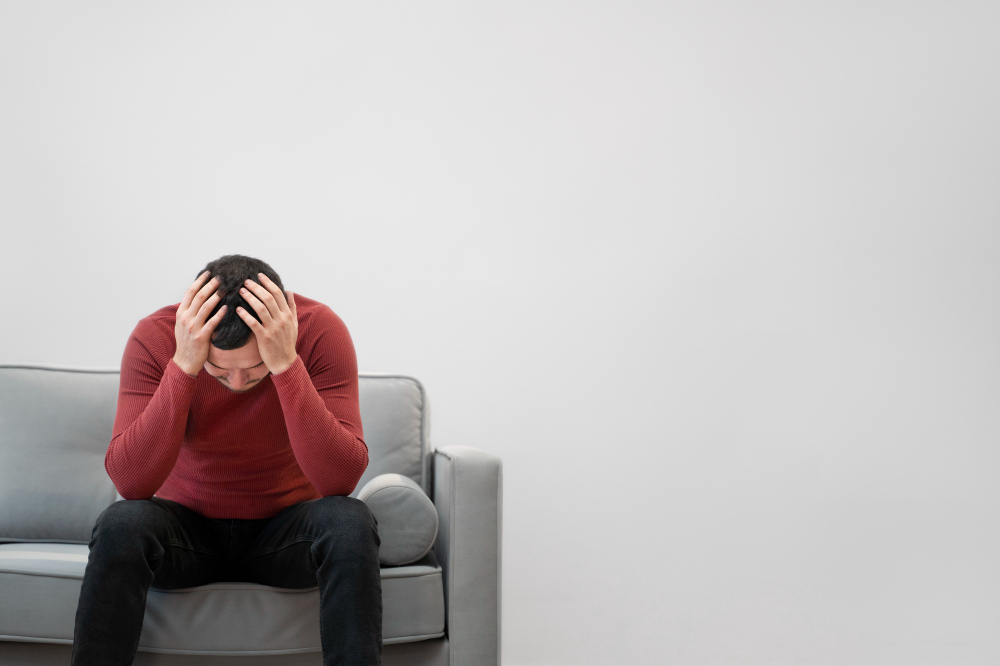

- Depression is a common and serious mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest or pleasure in activities. It can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life, affecting various aspects such as work, relationships, and physical health.
- Risk factors for depression include genetic predisposition, changes in brain chemistry and function, trauma or stressful life events, chronic medical conditions, certain medications, and substance abuse. It can occur at any age and may manifest differently in different individuals.
- Treatment for depression typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle modifications, and support from loved ones. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy, helps individuals develop coping skills, challenge negative thought patterns, and address underlying issues contributing to their depression. Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), may be prescribed to help rebalance brain chemistry and alleviate symptoms. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy diet, adequate sleep, and social support can also play a crucial role in managing depression. It’s essential for individuals experiencing symptoms of depression to seek professional help for proper diagnosis and treatment tailored to their specific needs.