Thyroid Disorders
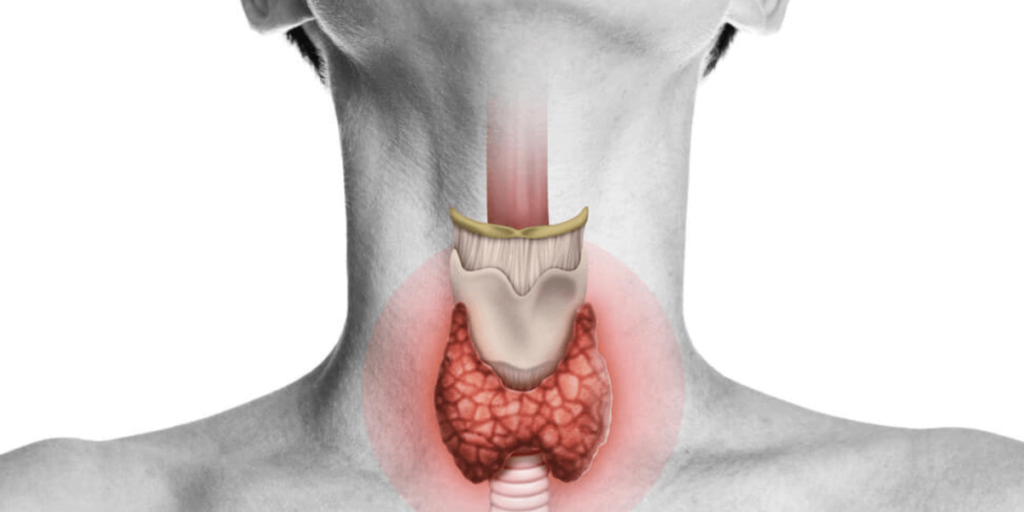
- Thyroid disease encompasses a range of disorders affecting the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that regulates metabolism and various bodily functions. Common thyroid conditions include hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer.
- Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, and depression. Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, results from an excess of thyroid hormone production and can cause symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, heat intolerance, tremors, and anxiety.
- Diagnosis of thyroid disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T4, and T3), and imaging studies such as ultrasound or thyroid scans. Treatment depends on the specific thyroid disorder and may include thyroid hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism, medications to block hormone production or radioactive iodine therapy for hyperthyroidism, surgical removal of nodules or thyroid cancer, or close monitoring for benign thyroid nodules. Regular follow-up care and monitoring of thyroid function are essential for managing thyroid disease and optimizing long-term outcomes.